







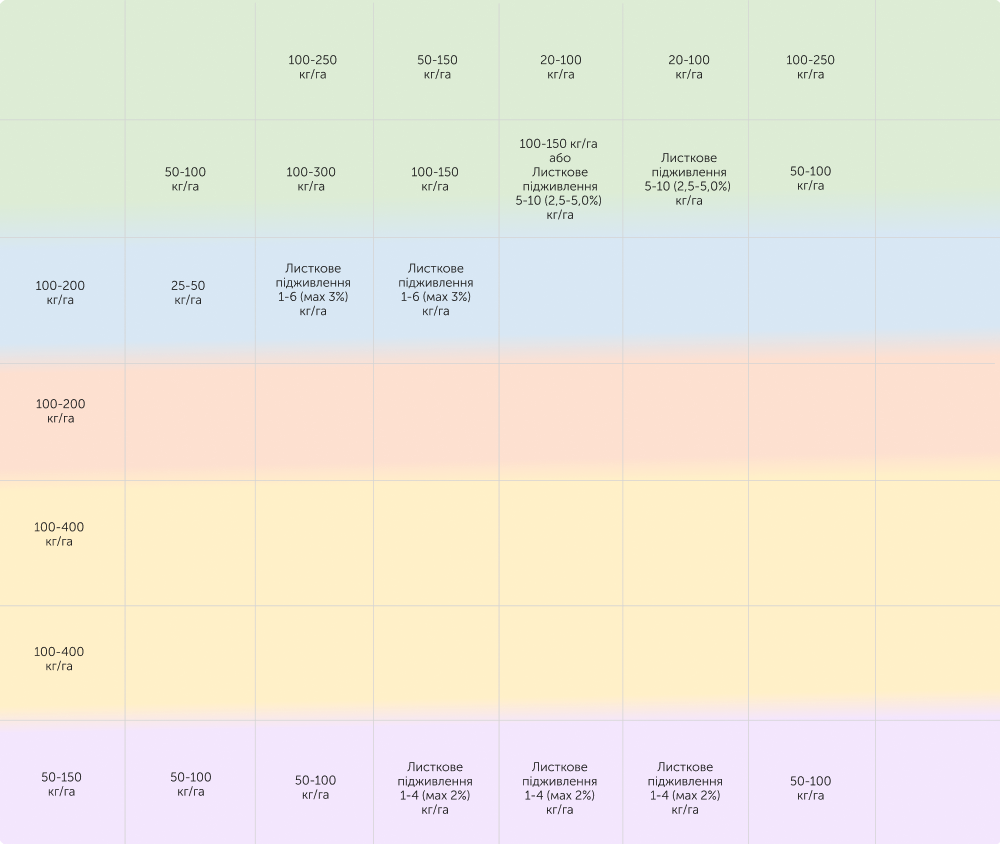
Principles of application
Winter wheat is the most demanding in terms of growing conditions and nutrients supply among winter cereals. To get 1 ton of grain with the corresponding amount of byproduct, crop consumes on average of 29 kg of nitrogen, 12 kg of phosphorous, 25 kg of potassium, 4 kg of Sulphur and other elements: calcium, magnesium, ferrum, manganese, zinc and copper.
During basal application it is recommended to apply maximum amount of phosphorous and potassium. Phosphorous improves development of root system and along with potassium enhance accumulation of storage materials and better overwintering.
If necessary, phosphorous can also be applied as a starter not exceeding the rate of 10-15 kg/ha P2O5 or compound N15-30P10-15 .
Feeding with phosphorous-potassium fertilizers is less effective.
Nitrogen fertilizers are effective for application in all seasons. In case of basal and at sowing application it is better to apply nitrogen in form of ammonia not exceeding 30 kg/ha of N. All forms of N are applicable for feeding. Feeding with nitrogen is better to apply fractionally taking into account plants development and current conditions. The crop’s greatest demand for N raises during booting.
To get winter wheat yield of 7-8 tons it is recommended to apply 150-180 kg/hа of N, 60-90 kg/hа of P2O5 and 120-150 kg/hа of K2O.